For starters, my absence the prior week was for naught. When your wife starts sounding like the second coming of Arnold Schwarzenneger and your own voice reverts to prepubescent days, you know the flu game is strong this season. Feeling under the weather is not enough to describe the hell that has been the past week, but here I am now, and all the merrier to finally be over with it.
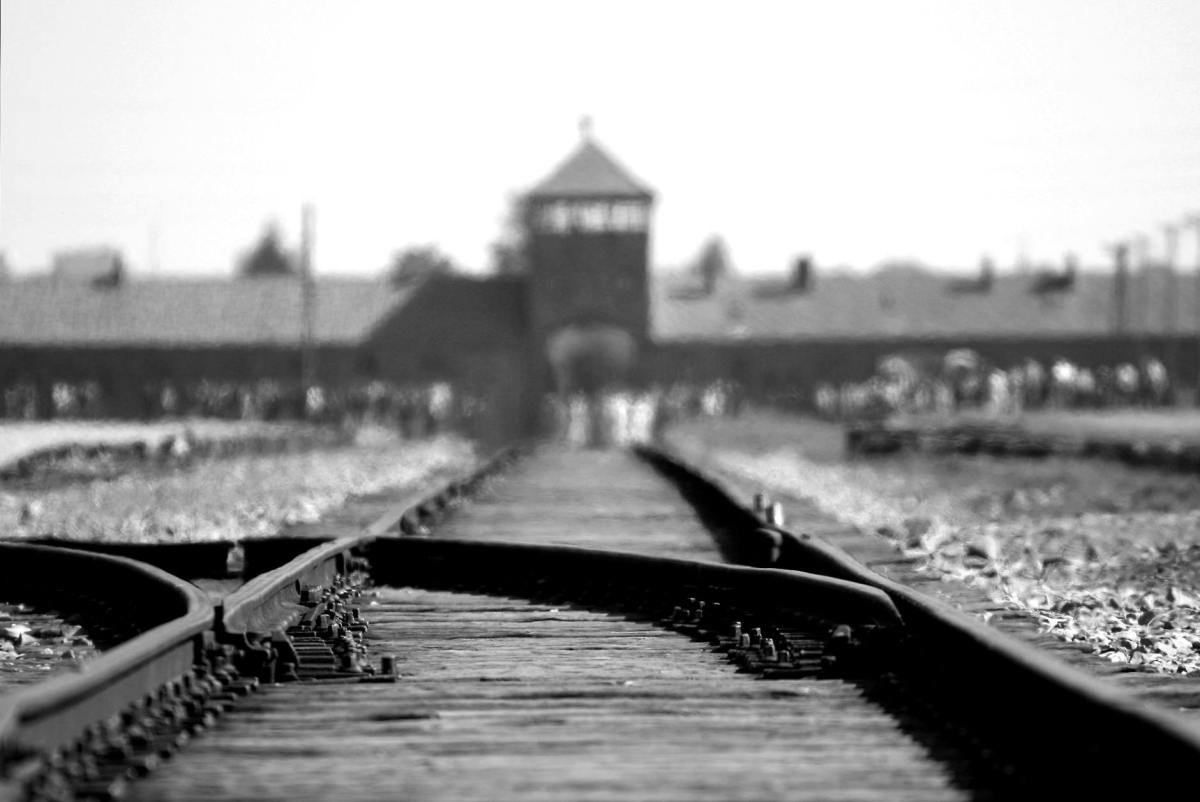
That being said, today’s post relays what went missing earlier. Falling sick gives you a good reason to relax. After all, rest is the best medicine. While the flu had destroyed my voice, my mental faculties remained sharp, and I had a lot to introspect about. Earlier, during my weekly visit to the local public library, I learned that January 27th observed International Holocaust Remembrance Day. Across from the reception desk was a table with several books and graphic novels related to the Holocaust. Perusing the selection reminded me of the last time I had read a book on the same topic. That was all the way back in high school.
From Art Spiegelman’s Maus to Elie Wiesel’s Night, my younger self had retreated in horror learning about the Holocaust. Wiesel’s graphic descriptions of his own survival at Auschwitz and Buchenwald had given me nightmares. The depravity that was in full flow leapt off the pages recounting the experiences of Holocaust victims. Those experiences also spoke to the enduring strength of those who survived and remain to this day.
That day at the library, I felt compelled to be drawn back into said world, now seemingly lost to memory. I picked out two titles that I found intriguing:


A few days later, I fell sick with the flu and spent my time reading the two books. My younger self had struggled to come to terms with the reality of the Holocaust, but as an adult, I felt more pensive revisiting this chapter in human history.
Who Owns the Clouds? and The Librarian of Auschwitz related the experiences of two young female protagonists, the impact the war and the Holocaust had on their families, their childhood, and their future. (Of course, there is a lot more to it, but I don’t want to give it all away; I highly recommend both titles!) Both protagonists undergo profound personal transformations (not always positive) that help them survive this tumultuous period of human affairs. The Holocaust is a telling moment in history that demonstrated the human capacity to inflict suffering and destruction. The subsequent horror took different forms in every generation. Both these books provide plenty of that, but that isn’t all there is to their purpose. Despite being two very different experiences, the two stories reitereate that even in the darkest of moments, not all is lost. The protagonists are uplifted by the actions of those who were courageous enough to stand up for their beliefs, to fight the good fight, and instill hope for the future.
My reading wasn’t a continuous process. I had to take breaks, and not for lack of focus, but due to frequent visits from my daughter, who took it upon herself to take care of her supposedly “ailing” father. Observing my daughter’s actions, I couldn’t help but juxtapose the protagonists’ realities onto hers. How would I react if something similar happened to my daughter? How would I protect her from a world that is torn asunder? It was not a pleasant thought, and it probably aggregated from a source of concern that has been on my mind of late.
Currently, there just doesn’t seem to be a pause button for the chaos unfolding across the world. Differences speak louder, and unity seems trivial. Social media has become a global echo chamber for negativity. Fall into this rabbit hole, and you are not coming out of it in one piece. As a person of color, I have experienced my fair share of racism and segregation. Now, here was my daughter, growing up as a biracial kid in a world where diversity was an excuse for division. What could I do to keep my daughter safe? What could I do to ensure that she would neither be a victim nor an instigator of the same negativity that seems to be running rampant in a global period of uncertainty and rapidly changing political landscapes (much like the history related by the books I had just read)?
It was not easy to mull these things over while battling the flu. Writing about it, I guess, is my way of finding courage and staying hopeful. It also helped that my daughter had all the answers. Much like the protagonists in the two books, whose innocence empowers their actions and guides them through their trials to do what is right, I found strength in my daughter’s actions. In a misplaced belief that I had fallen ill because of her, my daughter forced me to accept an apology on her part, later going on to reaffirm the importance of saying “Sorry” when one is at fault.
There was my answer. Making mistakes is part of being human, but it is more important to remember and learn from our faults. History teaches us a lot, and while it may seem distant from our present, the lessons of our past can help us move forward. This resonates with the discord of today’s global affairs and how the world just seems to want to tear itself up. Differences aren’t what set us apart, they serve as a gateway to connection and strength. It is in our courage to bridge them that we define our humanity.
Between stimulus and response there is a space. In that space is our power to choose our response. In our response lies our growth and our freedom. – Victor Frankl






 The concept of time has been central to the growth, and evolution of human civilizations. It has also served as an important facet of knowledge that has been studied to a great effect in religion, philosophy, and science. But, to this day, an absolute definition of time still evades scholars.
The concept of time has been central to the growth, and evolution of human civilizations. It has also served as an important facet of knowledge that has been studied to a great effect in religion, philosophy, and science. But, to this day, an absolute definition of time still evades scholars.


.jpg)